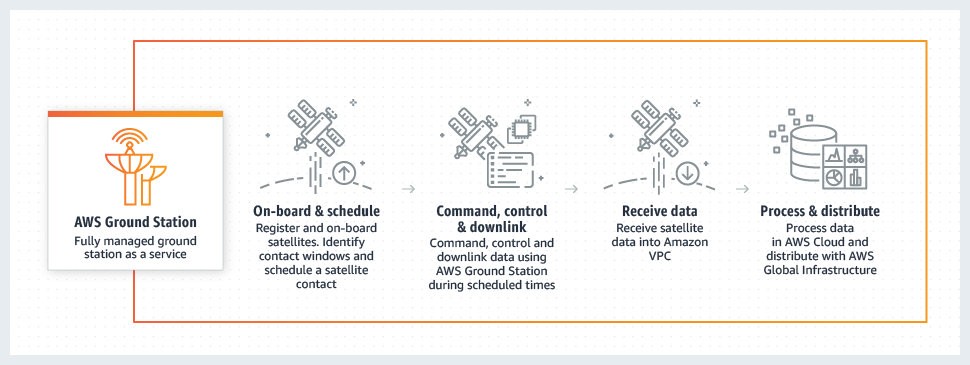
Amazon Web Services Inc. (AWS), an Amazon.com company, announced Thursday general availability of AWS Ground Station, a new service that makes it easy and cost-effective for customers to control satellites from AWS and download data from satellites into AWS Global Infrastructure Regions using a fully managed network of ground station antennas located around the world.
Once customers upload satellite commands and data through AWS Ground Station, they can quickly download large amounts of data over the high-speed AWS Ground Station network, immediately process it in an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance, store it in Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), apply AWS analytics and machine learning services to gain insights, and use Amazon’s network to move the data to other regions and processing facilities.
AWS Ground Station provides direct access to AWS services and the AWS Global Infrastructure including a low-latency global fiber network located where your data is downlinked into the AWS Ground Station. This enables users to control satellite communications, ingest and process satellite data, and rapidly integrate that data with applications and other services running in the AWS Cloud.
Getting started with AWS Ground Station takes just a few clicks in the AWS Management Console to schedule antenna access time and launch an Amazon EC2 instance to communicate with the satellite. There are no up-front payments or long-term commitments, no ground infrastructure to build or manage, and customers pay-by-the-minute for antenna access time used.
Satellites are being used by more and more businesses, universities, and governments for a variety of applications, including weather forecasting, surface imaging, and communications.
To do this, customers must build or lease ground antennas to communicate with the satellites. This is a significant undertaking and cost because customers often require antennas in multiple countries to download data when and where they need it without waiting for the satellite to pass over a desired location, and antennas are just the beginning of the infrastructure requirements because customers need servers, storage, and networking in close proximity to the antenna to process, store, and transport the data from the satellite.
As customers build business rules and workflows to organize, structure, and route the data to employees or customers before it can be used to deliver value. This requires significant capital investments and operational costs to build, manage, and securely maintain antennas, compute infrastructure, and business logic at each antenna location.
AWS Ground Station allows customers to more cost-effectively control satellite operations, ingest satellite data, and integrate the data with applications and other cloud services running in AWS.
Using AWS Ground Station, customers can save up to 80 percent of their ground station costs by paying for antenna access time on demand, and they can rely on AWS Ground Station’s growing global footprint of ground stations to downlink data when and where they need it. These ground stations are also located in close proximity to AWS Regions around the world, so customers can store, process, and analyze the data locally, rapidly gain insights, and then quickly take action.
The recency of data is particularly critical when it comes to tracking and acting upon fast-moving conditions on the ground. This timeliness depends on frequent communications between ground stations and satellites, which can only be achieved with a large, global footprint of antennas maintaining frequent contact with orbiting satellites.
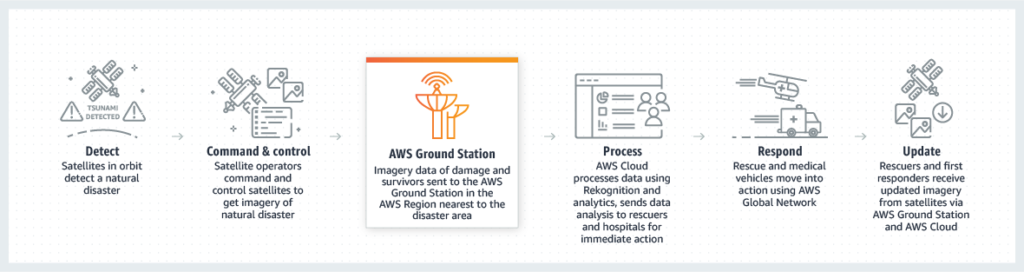
For example, as fast-moving environmental, geopolitical, or news events unfold on the ground, AWS Ground Station customers can downlink current data to any of the AWS ground stations around the world. Customers can get timely data sooner, rapidly experiment with new applications, and deliver products to market faster without buying, leasing, or maintaining complex and expensive antennas and infrastructure.
“Satellite data offers customers a profound way to build applications that help humans explore space and improve life on Earth, but the cost and difficulty of building and maintaining the infrastructure necessary to downlink and process the data has historically been prohibitive for all but the most well-funded organizations,” says Shayn Hawthorne, General Manager, AWS Ground Station. “The goal of AWS Ground Station is to make space communications ubiquitous and to make ground stations simple and easy to use, so that more organizations can derive insights from satellite data to help improve life on Earth and embark on deeper exploration and discovery in space. Customers can rely on AWS Ground Station’s global footprint to downlink data when and where they need it, get timely data, and build new applications faster based on readily available satellite data, without having to buy, lease, and maintain complex and expensive infrastructure.”
AWS Ground Station’s self-service graphical interface makes it easy to identify downlink opportunities, communications windows, and schedule antenna time. This enables customers to review confirmed times in the console and cancel or reschedule prior to the scheduled contact time. Because AWS Ground Station antennas are located in close proximity to AWS Regions, customers have low-latency, local access to other AWS services to process and store data.
For example, they can use Amazon EC2 to control satellites and downlink data, store and share the data in Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS), Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS), or Amazon S3, use Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) for secure communications between Amazon EC2 instances and the AWS Ground Station antenna gateway, hunt for real-time business insights with Amazon Kinesis Data Streams and Amazon Elastic Map Reduce, apply machine learning algorithms and models with Amazon SageMaker, add image analysis with Amazon Rekognition, and improve data sets by combining satellite data with IoT sensor data from AWS IoT Greengrass.
AWS Ground Station is available immediately in US East (Ohio) and US West (Oregon) and will expand to additional regions and locations in the coming year.
Maxar Technologies, operator of the high-resolution, high-accuracy WorldView imaging constellation, is preparing for the launch of its next-generation satellite constellation, WorldView Legion, in 2021.
“The addition of WorldView Legion enables us to image the most rapidly changing areas on Earth more than 15 times per day and triple our capacity to collect 30 cm resolution imagery,” said Dr. Walter Scott, Maxar’s Chief Technology Officer. “AWS Ground Station will provide us with more opportunities and capacity to downlink and analyze the large amount of data WorldView Legion will be sending back to Earth, enabling us to extract insights from the data for our customers when and where it matters.”
Thales Alenia Space, drawing on more than 40 years of experience and a unique combination of skills, expertise and cultures, delivers cost-effective solutions for telecommunications, navigation, Earth observation, environmental management, exploration, science and orbital infrastructures.
Governments and private industry alike count on Thales Alenia Space to design satellite-based systems that provide anytime, anywhere connections and positioning, monitor Earth, enhance management of its resources, and explore our Solar System and beyond. Thales Alenia Space is excited to collaborate with AWS to expand its New Space leading technologies to address the ground segment, including providing additional tools and features for AWS Ground Station customers.
“We integrate our innovative leading space technologies with the ones from partners within our ecosystem, such as AWS Ground Station, to help customers optimize the use of our planet’s – and our solar system’s – resources and to help build a better, more sustainable life on Earth,” said Viktoria Otero del Val, SVP Strategy, M&A and New Business Initiatives at Thales Alenia Space.
Myriota is a satellite IoT connectivity provider that enables customers to send small messages at ultra-low cost from anywhere on Earth. By securely delivering data direct to a constellation of low Earth orbit nanosatellites, Myriota’s unique patented and proven technology provides IoT connectivity in locations where terrestrial providers cannot operate, including oceans and the Australian outback. As an AWS Partner, Myriota is already using AWS for its processing and cloud-based delivery.
“With massive scale, long battery life, and direct-to-orbit connectivity for IoT, Myriota is helping customers with vital applications, such as sensor telemetry, low-value asset tracking, and device monitoring and control,” said Dr. David Haley, chief technology officer for Myriota. “The AWS Ground Station Network provides an exciting opportunity to further increase operational efficiency and reliability for our customers at massive scale.”




